Have you ever wondered why some cattle farms thrive while others struggle with low productivity and constant health issues? One of the hidden culprits behind many of these challenges is parasites. Parasite infestations—both internal and external—can silently drain the health and productivity of cattle, leading to significant economic losses for farmers. In this article, we’ll explore the crucial role of parasite control in maintaining not only the well-being of your herd but also the profitability of your entire operation. By the end, you’ll learn how to effectively combat parasites, boost your farm’s productivity, and maximize your profits.
Understanding Parasites in Cattle Farming
Parasites are a constant threat to cattle, and they come in two main forms:
- Internal Parasites: These include gastrointestinal worms, liver flukes, and lungworms. They often affect the digestive and respiratory systems of cattle, leading to weight loss, reduced feed conversion, and even death in severe cases.
- External Parasites: Ticks, lice, flies, and mites fall into this category. These parasites typically infest the skin and can cause conditions like anemia, irritation, and infections. They can also transmit diseases such as anaplasmosis and babesiosis.
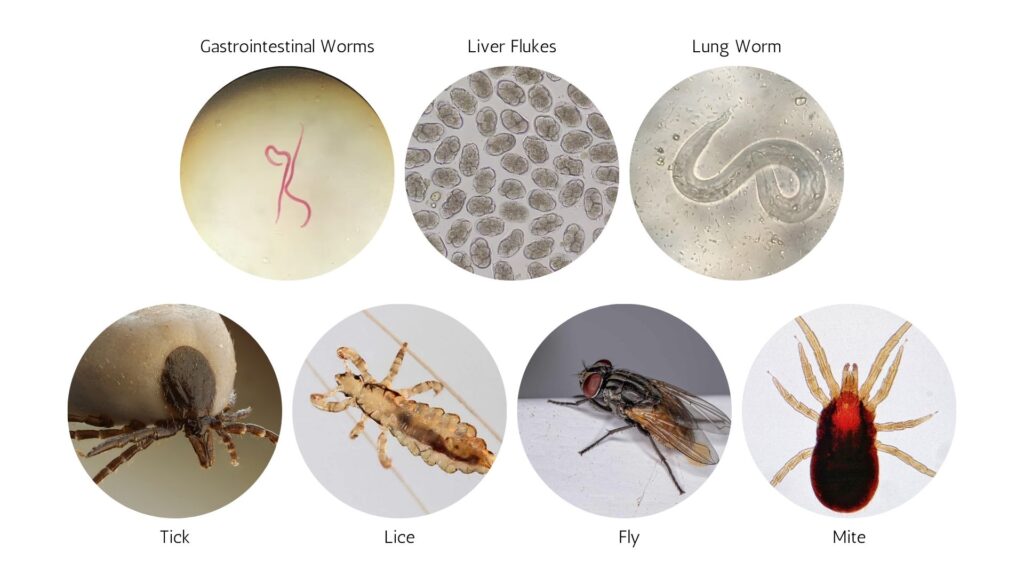
Signs of Parasite Infestations
Early detection is key to managing parasite load in cattle. Watch out for the following signs of parasitic infections:
- Weight loss or failure to gain weight despite adequate feeding.
- Dull or rough coat.
- Diarrhea and poor body condition.
- Coughing (in the case of lungworms).
- Visible signs of external parasites like ticks or lice.
Without proper control, these parasites can drastically reduce the productivity of your herd, leading to significant financial losses.
Economic Impact of Parasite Infestations
One of the main reasons parasite control is crucial in cattle farming is the economic impact these infestations have. Parasites reduce the efficiency of cattle to convert feed into weight gain or milk production. They also affect reproductive success, meaning fewer calves and lower milk yield per cow. The combined effects lead to reduced productivity and profitability.
Key Ways Parasites Cause Financial Loss:
- Reduced Growth Rates: Parasite infestations drain nutrients from cattle, which decreases growth rates. This means cattle take longer to reach market weight, requiring more feed and extending the time to sale.
- Lower Milk Production: Lactating cows under parasite stress produce less milk, reducing income for dairy farmers.
- Increased Veterinary Costs: Left unchecked, parasites can lead to severe health problems requiring expensive treatments or even culling of cattle, further decreasing herd size and profitability.
- Carcass and Hide Damage: External parasites like lice and ticks damage the skin and hides of cattle, lowering their value in the market. Additionally, the carcass quality may suffer, decreasing its marketability.
The Role of Parasite Control in Improving Herd Health
A herd free of parasites is a healthier, more productive herd. Healthy cattle are more resilient to disease, produce more milk, and grow at optimal rates, all of which directly impact profitability.
Benefits of Parasite Control for Herd Health:
- Improved Weight Gain: Cattle are able to gain weight faster, reaching market size sooner and with fewer resources.
- Increased Milk Yield: Healthy cows produce more milk, improving overall dairy farm profitability.
- Better Reproductive Performance: Parasite control reduces the risk of abortions, weak calves, and infertility, leading to a more productive herd.
- Reduced Disease Transmission: Many parasites are vectors for serious diseases. Effective control reduces the likelihood of these diseases spreading within the herd.
In a study involving dairy farms, farms that implemented regular parasite control programs saw a 10-15% increase in milk production compared to farms that didn’t, illustrating how crucial parasite management is for profitability.
Effective Parasite Control Strategies for Cattle Farmers
There are several strategies farmers can adopt to control parasites in their herds. These strategies range from preventive measures to treatments and should be tailored to the specific needs of each farm.
1. Preventive Measures:
- Pasture Rotation: Rotating pastures can help reduce the exposure of cattle to parasitic larvae that develop in the soil. It also helps disrupt the life cycle of many parasites.
- Clean Water and Feed Sources: Ensuring cattle have access to clean water and uncontaminated feed reduces the chances of parasite transmission.
- Nutritional Management: Well-nourished cattle have stronger immune systems, making them more resistant to parasites.
2. Treatment Options:
- Deworming: Use anthelmintics (dewormers) at strategic points in the year to control internal parasites. Always consult with a veterinarian to select the right product and dosing schedule.
- Topical and Injectable Treatments: For external parasites, options like pour-on insecticides and injectable treatments are available.
- Oral Medications: Some oral medications target both internal and external parasites, offering a broad spectrum of protection.
3. Monitoring and Professional Advice:
- Regular fecal testing to monitor internal parasite load.
- Consult with a veterinarian to develop a farm-specific parasite control program.
Sustainable Parasite Control Practices
As with any management practice, sustainability is key for long-term success. Overuse of chemical treatments can lead to resistance in parasites, rendering common products ineffective over time. To avoid this, cattle farmers should consider integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
Key Components of Sustainable Parasite Control:
- Rotate Dewormers: Using the same dewormer repeatedly can lead to resistance. Rotate between different classes of anthelmintics to prevent this.
- Natural and Organic Methods: Consider natural dewormers like diatomaceous earth or garlic to reduce chemical use. These can be part of a broader control program, especially for organic farms.
- Pasture Management: Keep pastures well-managed and rotate them regularly to avoid overgrazing and the buildup of parasite larvae.
By adopting sustainable practices, farmers can ensure their parasite control efforts remain effective and cost-efficient in the long term.
How Parasite Control Leads to Higher Profits
A well-implemented parasite control program pays off in tangible ways. Cattle that are free of parasites grow faster, produce more, and are generally healthier, leading to lower vet bills and higher overall productivity.
Key Profit Drivers of Parasite Control:
- Increased Productivity: Healthier cattle reach market weight faster and produce more milk.
- Better Market Prices: Parasite-free cattle are more attractive to buyers, often fetching higher prices.
- Lower Treatment Costs: Preventing infestations reduces the need for expensive veterinary treatments.
In a study of beef cattle farms, farms that consistently managed parasites reported a 15-20% higher return on investment (ROI) compared to those that didn’t, proving the financial benefits of a strong parasite control program.
Working with Veterinarians to Develop a Parasite Control Plan
Veterinarians are valuable partners in developing a parasite control plan tailored to your farm’s specific conditions. Regular check-ups and consultations will ensure that the chosen methods are effective and up-to-date.
How Veterinarians Help:
- Customized Programs: Vets can create a parasite control plan that fits your specific herd, environment, and parasite challenges.
- Regular Monitoring: Fecal egg counts and other tests help determine the parasite burden and the effectiveness of treatments.
Conclusion: Parasite Control is Key to Cattle Farming Success
Parasite control is more than just a health concern—it’s a strategic move for long-term profitability in cattle farming. Throughout this post, we’ve covered the types of parasites that affect cattle, the economic impact they can have, and the strategies to prevent and manage infestations. By implementing sustainable parasite control measures, farmers can protect their herd’s health, boost productivity, and reduce financial losses.
Prioritizing parasite control not only improves cattle performance but also leads to a stronger bottom line. The sooner you take control of parasites, the sooner you’ll see the benefits in your herd and your profits.
Ready to take your herd’s health to the next level? Explore our website for a wide range of animal health products, including disinfectants, vaccines, and other essential animal medicaments to support your parasite control efforts and overall farm success.